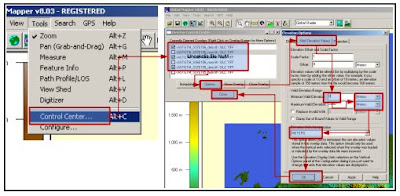
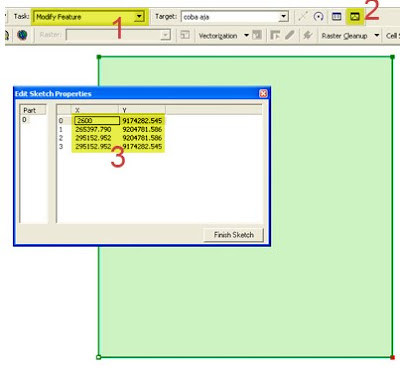
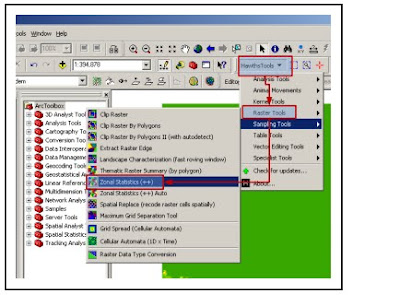
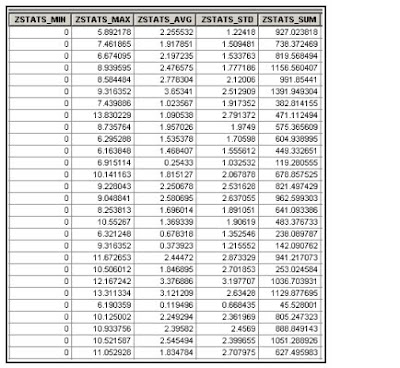
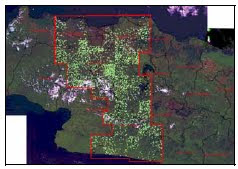
Map Trans JOgja
Trans Jogja is one of the alternative public transport which is very popular among maysrakat Jogja. For students who have long or just stay in Jogja is quite affordable mode of transportation for students pocket. With the price of a single fare ticket Rp.3000 Transjogja offering cheap transportation convenience with no record of all the places we are close to the boarding Transjogja stop. Please check or donwload any path through the area where you live
Line 1 A Prambanan Airport Adisutjipto Jackie Flyover Ambarrukmo Plaza UIN Sunan Kalijaga Saphir Square Cinema XXI, Jl. Solo Bethesda Hospital, Scholastic Book Store, Hotel Novotel Hotel Santika, Pizza Hut Webcam Office of the People's Sovereignty Jogjakarta Tugu Station Jalan Malioboro (there are 3 pieces stops) Post Office, the Palace, North Square, Monument March 1, Vredeburg Taman Pintar, State Bank parking Indonesia, Market Beringhardjo, Gondomanan Market Sentul (Jl. State Students) Parks Eating Heroes Kusumanegara Hall Jogjakarta Excited Loka Zoo Jogja Expo Center Jackie Bridges (back toward Kalasan, Adisutjipto Airport to Terminal Prambanan) Trans Jogja Line 1B Terminal Prambanan Kalasan Adisucipto Airport Maguwoharjo Jackie (passed down) Block O JEC Babadan Gedongkuning Excited Loka SGM Sentul market Gondomanan Post Office RS.PKU Muhammadiyah Flower Market Badran Roundabout SAMSAT Pingit Monument Scholastic UGM roundabout Colombo Demangan UIN Sunan Kalijaga Jackie Maguwoharjo Bandra Adisucipto Kalasan Terminal Prambanan. Trans Jogja Line 2A Terminal Mount Wilson Monjali Monument Tugu Station Malioboro Post Office Gondomanan Jokteng Wetan Tungkak Gambiran Basen Rejowinangun Babadan Gedongkuning Excited Loka SGM Sandalwood Mandala Krida Gayam Flyover Lempuyangan Kridosono Ambassador Discourse Galeria Scholastic UGM roundabout Colombo Terminal Condongcatur Kentungan Monjali Terminal Mount Wilson Trans Jogja Line 2B Terminal Mount Wilson Monjali Kentungan Lean Terminal Chess Colombo UGM roundabout Scholastic Kridosono Ambassador Discourse Fly-over Lempuyangan Gayam Mandala Krida Sandalwood SGM Gembiraloka Babadan Gedongkuning Rejowinangun Basen Tungkak Joktengwetan Gondomanan Post Office PKU Muhammadiyah Hospital Ngabean Wirobrajan CPC Badran Roundabout SAMSAT Pingit Monument Monjali Terminal Mount Wilson. Trans Jogja 3A Line Terminal Giwangan Tegalgendu HS-Silver Jl. Nyi Pembayun Pawnshop Kotagede Basen Rejowinangun Babadan Gedongkuning JEC Block O Jackie (pass on) Jackie Maguwoharjo Adisucipto Airport Maguwoharjo North Ringroad Terminal Condongcatur Kentungan MM UGM MirotaKampus Gondolayu Monument Pingit Roundabout SAMSAT Badran PasarKembang TUGU Station Malioboro Post Office PKU Muhammadiyah Hospital Ngabean Jokteng Kulon Ivory Plengkung Jokteng Wetan Tungkak Wirosaban Tegalgendu Terminal Giwangan. Trans Jogja Line 3B Terminal Giwangan Tegalgendu Wirosaban Tungkak Jokteng Wetan Ivory Plengkung JoktengKulon Ngabean PKU Muhammadiyah Hospital Flower Market Badran Roundabout SAMSAT Pingit Monument Gondolayu Mirota Campus MM UGM Kentungan Lean Terminal Chess North Ringroad Maguwoharjo Adisucipto Airport Maguwoharjo Jackie (passed down) Block O JEC Babadan Gedongkuning Rejowinangun S3. Basen Pawnshop Kotagede Jl.Nyi Pembayun HS-Silver Tegalgendu Terminal Giwangan. Trans Jogja Line 4A Terminal Giwangan SMK Muhammadiyah 3 Biology Museum Hayam Wuruk SMPN 5 Puro Pakualaman Student Park Ahmad Dahlan University Terminal Giwangan. Trans Jogja Line 4B Terminal Giwangan SMK Muhammadiyah 3 Kusumanegara 3 SGM STPMD 1 UIN Sunan Kalijaga 1 Women Building LPP Sudirman 1 SMPN 5 AA YKPN De Britto UIN Sunan Kalijaga 2 STPMD 2 SMKN 5 Kusumanegara 4 Art Market Ahmad Dahlan University Terminal Giwangan
Trans Jogja is one of the alternative public transport which is very popular among maysrakat Jogja. For students who have long or just stay in Jogja is quite affordable mode of transportation for students pocket. With the price of a single fare ticket Rp.3000 Transjogja offering cheap transportation convenience with no record of all the places we are close to the boarding Transjogja stop. Please check or donwload any path through the area where you live
Line 1 A Prambanan Airport Adisutjipto Jackie Flyover Ambarrukmo Plaza UIN Sunan Kalijaga Saphir Square Cinema XXI, Jl. Solo Bethesda Hospital, Scholastic Book Store, Hotel Novotel Hotel Santika, Pizza Hut Webcam Office of the People's Sovereignty Jogjakarta Tugu Station Jalan Malioboro (there are 3 pieces stops) Post Office, the Palace, North Square, Monument March 1, Vredeburg Taman Pintar, State Bank parking Indonesia, Market Beringhardjo, Gondomanan Market Sentul (Jl. State Students) Parks Eating Heroes Kusumanegara Hall Jogjakarta Excited Loka Zoo Jogja Expo Center Jackie Bridges (back toward Kalasan, Adisutjipto Airport to Terminal Prambanan) Trans Jogja Line 1B Terminal Prambanan Kalasan Adisucipto Airport Maguwoharjo Jackie (passed down) Block O JEC Babadan Gedongkuning Excited Loka SGM Sentul market Gondomanan Post Office RS.PKU Muhammadiyah Flower Market Badran Roundabout SAMSAT Pingit Monument Scholastic UGM roundabout Colombo Demangan UIN Sunan Kalijaga Jackie Maguwoharjo Bandra Adisucipto Kalasan Terminal Prambanan. Trans Jogja Line 2A Terminal Mount Wilson Monjali Monument Tugu Station Malioboro Post Office Gondomanan Jokteng Wetan Tungkak Gambiran Basen Rejowinangun Babadan Gedongkuning Excited Loka SGM Sandalwood Mandala Krida Gayam Flyover Lempuyangan Kridosono Ambassador Discourse Galeria Scholastic UGM roundabout Colombo Terminal Condongcatur Kentungan Monjali Terminal Mount Wilson Trans Jogja Line 2B Terminal Mount Wilson Monjali Kentungan Lean Terminal Chess Colombo UGM roundabout Scholastic Kridosono Ambassador Discourse Fly-over Lempuyangan Gayam Mandala Krida Sandalwood SGM Gembiraloka Babadan Gedongkuning Rejowinangun Basen Tungkak Joktengwetan Gondomanan Post Office PKU Muhammadiyah Hospital Ngabean Wirobrajan CPC Badran Roundabout SAMSAT Pingit Monument Monjali Terminal Mount Wilson. Trans Jogja 3A Line Terminal Giwangan Tegalgendu HS-Silver Jl. Nyi Pembayun Pawnshop Kotagede Basen Rejowinangun Babadan Gedongkuning JEC Block O Jackie (pass on) Jackie Maguwoharjo Adisucipto Airport Maguwoharjo North Ringroad Terminal Condongcatur Kentungan MM UGM MirotaKampus Gondolayu Monument Pingit Roundabout SAMSAT Badran PasarKembang TUGU Station Malioboro Post Office PKU Muhammadiyah Hospital Ngabean Jokteng Kulon Ivory Plengkung Jokteng Wetan Tungkak Wirosaban Tegalgendu Terminal Giwangan. Trans Jogja Line 3B Terminal Giwangan Tegalgendu Wirosaban Tungkak Jokteng Wetan Ivory Plengkung JoktengKulon Ngabean PKU Muhammadiyah Hospital Flower Market Badran Roundabout SAMSAT Pingit Monument Gondolayu Mirota Campus MM UGM Kentungan Lean Terminal Chess North Ringroad Maguwoharjo Adisucipto Airport Maguwoharjo Jackie (passed down) Block O JEC Babadan Gedongkuning Rejowinangun S3. Basen Pawnshop Kotagede Jl.Nyi Pembayun HS-Silver Tegalgendu Terminal Giwangan. Trans Jogja Line 4A Terminal Giwangan SMK Muhammadiyah 3 Biology Museum Hayam Wuruk SMPN 5 Puro Pakualaman Student Park Ahmad Dahlan University Terminal Giwangan. Trans Jogja Line 4B Terminal Giwangan SMK Muhammadiyah 3 Kusumanegara 3 SGM STPMD 1 UIN Sunan Kalijaga 1 Women Building LPP Sudirman 1 SMPN 5 AA YKPN De Britto UIN Sunan Kalijaga 2 STPMD 2 SMKN 5 Kusumanegara 4 Art Market Ahmad Dahlan University Terminal Giwangan


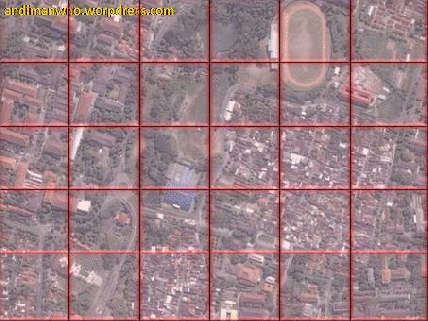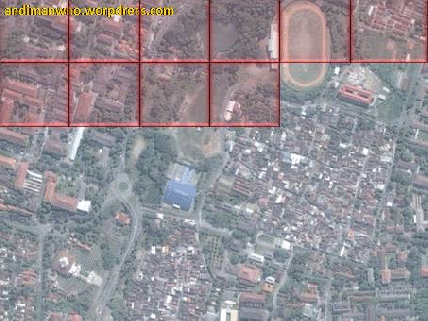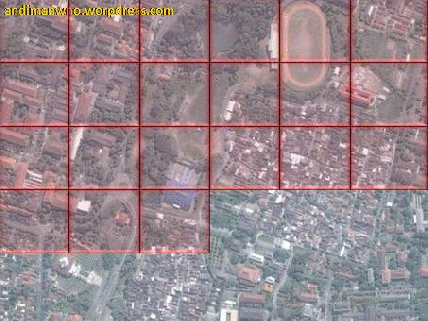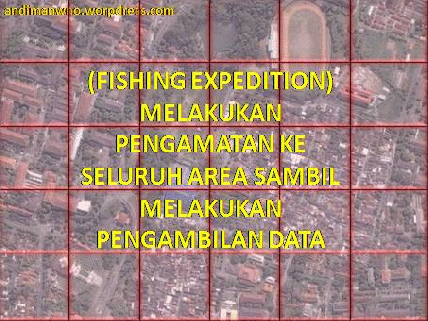 2. logical Search
In this method of observation of the entire region in image retrieval is only performed but is selective in certain areas in accordance with the purpose of interpretation.
2. logical Search
In this method of observation of the entire region in image retrieval is only performed but is selective in certain areas in accordance with the purpose of interpretation.
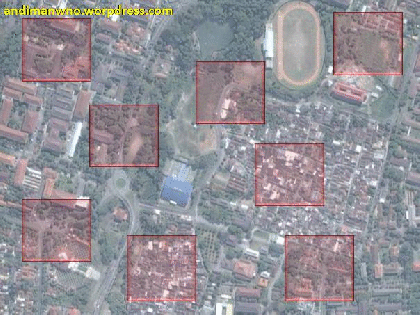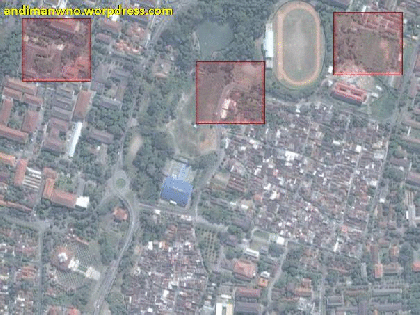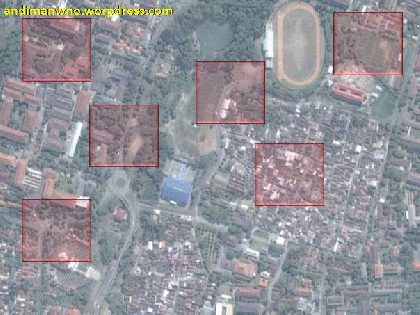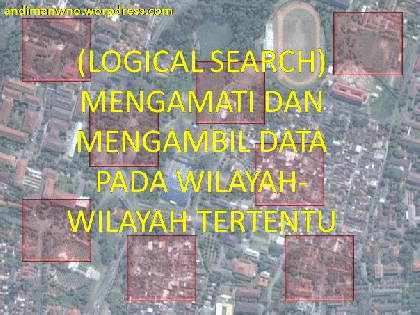

 used to conduct Image Interpretation
General steps taken to acquire remote sensing data that can be utilized by a variety of fields are:
1. detection
At this stage object detection activities recorded on aerial photographs and satellite images
2. identification
Mengidentifikai object by its characteristic spectral, spatial and temporal.
3. introduction
Object recognition is done in order to classify the object shown in the image based on specific knowledge
4. analysis
The analysis aims to group objects that have the same characteristics
5. deduction
An object based image processing activities contained in the image to a more specific.
6. classification
Includes descriptions and restrictions (delineation) of the objects contained in the image
7. idealization
Presentation of the results of image interpretation of data in the form of a ready-made maps.
used to conduct Image Interpretation
General steps taken to acquire remote sensing data that can be utilized by a variety of fields are:
1. detection
At this stage object detection activities recorded on aerial photographs and satellite images
2. identification
Mengidentifikai object by its characteristic spectral, spatial and temporal.
3. introduction
Object recognition is done in order to classify the object shown in the image based on specific knowledge
4. analysis
The analysis aims to group objects that have the same characteristics
5. deduction
An object based image processing activities contained in the image to a more specific.
6. classification
Includes descriptions and restrictions (delineation) of the objects contained in the image
7. idealization
Presentation of the results of image interpretation of data in the form of a ready-made maps.